Voice MCP
by mbailey
Voice Mode enables natural voice conversations with AI assistants like Claude and ChatGPT, integrating human-like voice interactions through the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Voice MCP Overview
What is Voice Mode?
Voice Mode is a tool that brings natural, human-like voice conversations to AI assistants such as Claude, ChatGPT, and other Large Language Models (LLMs). It achieves this by integrating with the Model Context Protocol (MCP), allowing users to interact with their AI through speech rather than text.
How to use Voice Mode?
Voice Mode can be installed via uvx, pip, or from source. It requires Python 3.10+ and an OpenAI API Key (or compatible service) for speech-to-text and text-to-speech. Users can integrate Voice Mode with various AI coding assistants like Claude Code, Claude Desktop, Gemini CLI, Cursor, VS Code, and more by configuring their respective MCP settings. Once configured, users can initiate voice conversations with their AI assistant, using commands like claude converse.
Key Features of Voice Mode
- Voice conversations: Engage in natural voice interactions with AI assistants, asking questions and receiving spoken responses.
- Multiple transports: Supports local microphone input and LiveKit room-based communication.
- OpenAI-compatible: Works seamlessly with any OpenAI-compatible Speech-to-Text (STT) and Text-to-Speech (TTS) services, both local and cloud-based.
- Real-time interaction: Provides low-latency voice interactions with automatic transport selection for a fluid experience.
- MCP Integration: Ensures seamless compatibility with Claude Desktop and other MCP clients.
- Silence detection: Automatically stops recording when the user stops speaking, enhancing conversational flow.
- Local STT/TTS support: Allows for privacy-focused or offline usage with local services like Whisper.cpp for STT and Kokoro for TTS.
Use Cases of Voice Mode
- Programming & Development: Debug errors verbally, walk through code explanations, brainstorm architectural designs, and get help writing tests through natural conversation.
- General Productivity: Practice presentations, organize thoughts, prepare for interviews with Q&A, and use the AI as a "rubber duck" for problem-solving.
- Voice Control Features: Control the AI with voice commands, such as "Read this error message" or "Just give me a quick summary," and use the
conversefunction for natural, back-and-forth interactions.
FAQ from Voice Mode
- What are the system requirements? Python 3.10+, Linux, macOS, or Windows (WSL), and an OpenAI API Key.
- How do I install Voice Mode? You can install it using
uvx voice-mode,pip install voice-mode, or by cloning the GitHub repository and installing from source. - Can I use local STT/TTS services? Yes, Voice Mode supports local services like Whisper.cpp for STT and Kokoro for TTS, offering privacy and offline capabilities.
- How do I configure Voice Mode with my AI coding assistant? Detailed integration guides are available for various tools like Claude Code, Cursor, VS Code, and more, typically involving adding Voice Mode to their MCP settings.
- What if I encounter audio issues? Check system permissions, ensure
uvis installed, verify your OpenAI API key, and use the provided diagnostic scripts for troubleshooting audio setup.
Voice MCP's README
Voice Mode
Install via:
uvx voice-mode|pip install voice-mode| getvoicemode.com
Natural voice conversations for AI assistants. Voice Mode brings human-like voice interactions to Claude, ChatGPT, and other LLMs through the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
🖥️ Compatibility
Runs on: Linux • macOS • Windows (WSL) | Python: 3.10+
✨ Features
- 🎙️ Voice conversations with Claude - ask questions and hear responses
- 🔄 Multiple transports - local microphone or LiveKit room-based communication
- 🗣️ OpenAI-compatible - works with any STT/TTS service (local or cloud)
- ⚡ Real-time - low-latency voice interactions with automatic transport selection
- 🔧 MCP Integration - seamless with Claude Desktop and other MCP clients
- 🎯 Silence detection - automatically stops recording when you stop speaking (no more waiting!)
🎯 Simple Requirements
All you need to get started:
- 🔑 OpenAI API Key (or compatible service) - for speech-to-text and text-to-speech
- 🎤 Computer with microphone and speakers OR ☁️ LiveKit server (LiveKit Cloud or self-hosted)
Quick Start
📖 Using a different tool? See our Integration Guides for Cursor, VS Code, Gemini CLI, and more!
npm install -g @anthropic-ai/claude-code
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
claude mcp add --scope user voice-mode uvx voice-mode
export OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-key
claude converse
🎬 Demo
Watch Voice Mode in action with Claude Code:
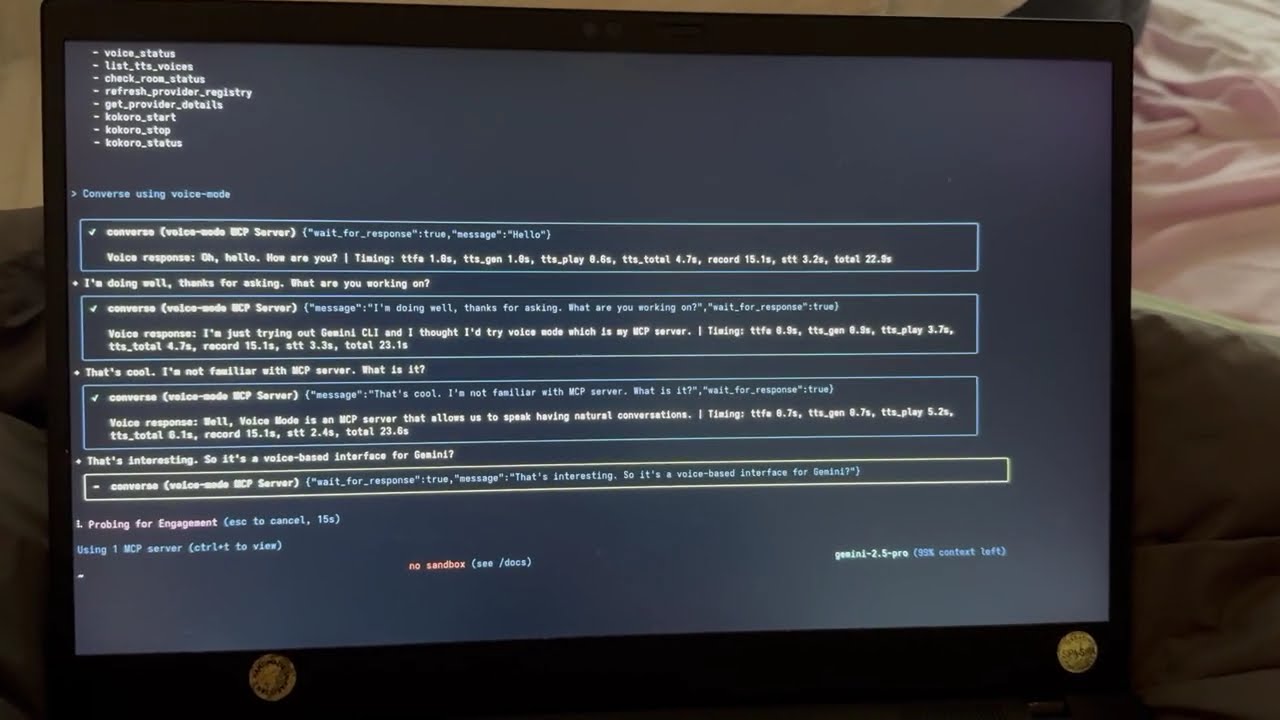
Voice Mode with Gemini CLI
See Voice Mode working with Google's Gemini CLI (their implementation of Claude Code):
Example Usage
Once configured, try these prompts with Claude:
👨💻 Programming & Development
"Let's debug this error together"- Explain the issue verbally, paste code, and discuss solutions"Walk me through this code"- Have Claude explain complex code while you ask questions"Let's brainstorm the architecture"- Design systems through natural conversation"Help me write tests for this function"- Describe requirements and iterate verbally
💡 General Productivity
"Let's do a daily standup"- Practice presentations or organize your thoughts"Interview me about [topic]"- Prepare for interviews with back-and-forth Q&A"Be my rubber duck"- Explain problems out loud to find solutions
🎯 Voice Control Features
"Read this error message"(Claude speaks, then waits for your response)"Just give me a quick summary"(Claude speaks without waiting)- Use
converse("message", wait_for_response=False)for one-way announcements
The converse function makes voice interactions natural - it automatically waits for your response by default, creating a real conversation flow.
Supported Tools
Voice Mode works with your favorite AI coding assistants:
- 🤖 Claude Code - Anthropic's official CLI
- 🖥️ Claude Desktop - Desktop application
- 🌟 Gemini CLI - Google's CLI tool
- ⚡ Cursor - AI-first code editor
- 💻 VS Code - With MCP preview support
- 🦘 Roo Code - AI dev team in VS Code
- 🔧 Cline - Autonomous coding agent
- ⚡ Zed - High-performance editor
- 🏄 Windsurf - Agentic IDE by Codeium
- 🔄 Continue - Open-source AI assistant
Installation
Prerequisites
- Python >= 3.10
- Astral UV - Package manager (install with
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh) - OpenAI API Key (or compatible service)
System Dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y python3-dev libasound2-dev libasound2-plugins libportaudio2 portaudio19-dev ffmpeg pulseaudio pulseaudio-utils
Note for WSL2 users: WSL2 requires additional audio packages (pulseaudio, libasound2-plugins) for microphone access. See our WSL2 Microphone Access Guide if you encounter issues.
sudo dnf install python3-devel alsa-lib-devel portaudio-devel ffmpeg
# Install Homebrew if not already installed
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# Install dependencies
brew install portaudio ffmpeg
Follow the Ubuntu/Debian instructions above within WSL.
Quick Install
# Using Claude Code (recommended)
claude mcp add --scope user voice-mode uvx voice-mode
# Using UV
uvx voice-mode
# Using pip
pip install voice-mode
Configuration for AI Coding Assistants
📖 Looking for detailed setup instructions? Check our comprehensive Integration Guides for step-by-step instructions for each tool!
Below are quick configuration snippets. For full installation and setup instructions, see the integration guides above.
claude mcp add voice-mode -- uvx voice-mode
Or with environment variables:
claude mcp add voice-mode --env OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-key -- uvx voice-mode
macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
Windows: %APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
Add to your Cline MCP settings:
Windows:
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": ["/c", "uvx", "voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
macOS/Linux:
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
Add to your .continue/config.json:
{
"experimental": {
"modelContextProtocolServers": [
{
"transport": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
]
}
}
Add to ~/.cursor/mcp.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
Add to your VS Code MCP config:
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
Add to your Zed settings.json:
{
"context_servers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": {
"path": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
}
- Open VS Code Settings (
Ctrl/Cmd + ,) - Search for "roo" in the settings search bar
- Find "Roo-veterinaryinc.roo-cline → settings → Mcp_settings.json"
- Click "Edit in settings.json"
- Add Voice Mode configuration:
{
"mcpServers": {
"voice-mode": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["voice-mode"],
"env": {
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "your-openai-key"
}
}
}
}
Alternative Installation Options
docker run -it --rm \
-e OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-key \
--device /dev/snd \
-v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
-e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY \
ghcr.io/mbailey/voicemode:latest
pipx install voice-mode
git clone https://github.com/mbailey/voicemode.git
cd voicemode
pip install -e .
Tools
| Tool | Description | Key Parameters |
|---|---|---|
converse |
Have a voice conversation - speak and optionally listen | message, wait_for_response (default: true), listen_duration (default: 30s), transport (auto/local/livekit) |
listen_for_speech |
Listen for speech and convert to text | duration (default: 5s) |
check_room_status |
Check LiveKit room status and participants | None |
check_audio_devices |
List available audio input/output devices | None |
start_kokoro |
Start the Kokoro TTS service | models_dir (optional, defaults to ~/Models/kokoro) |
stop_kokoro |
Stop the Kokoro TTS service | None |
kokoro_status |
Check the status of Kokoro TTS service | None |
Note: The converse tool is the primary interface for voice interactions, combining speaking and listening in a natural flow.
Configuration
- 📖 Integration Guides - Step-by-step setup for each tool
- 🔧 Configuration Reference - All environment variables
- 📁 Config Examples - Ready-to-use configuration files
Quick Setup
The only required configuration is your OpenAI API key:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-key"
Optional Settings
# Custom STT/TTS services (OpenAI-compatible)
export STT_BASE_URL="http://127.0.0.1:2022/v1" # Local Whisper
export TTS_BASE_URL="http://127.0.0.1:8880/v1" # Local TTS
export TTS_VOICE="alloy" # Voice selection
# Or use voice preference files (see Configuration docs)
# Project: /your-project/voices.txt or /your-project/.voicemode/voices.txt
# User: ~/voices.txt or ~/.voicemode/voices.txt
# LiveKit (for room-based communication)
# See docs/livekit/ for setup guide
export LIVEKIT_URL="wss://your-app.livekit.cloud"
export LIVEKIT_API_KEY="your-api-key"
export LIVEKIT_API_SECRET="your-api-secret"
# Debug mode
export VOICEMODE_DEBUG="true"
# Save all audio (TTS output and STT input)
export VOICEMODE_SAVE_AUDIO="true"
# Audio format configuration (default: pcm)
export VOICEMODE_AUDIO_FORMAT="pcm" # Options: pcm, mp3, wav, flac, aac, opus
export VOICEMODE_TTS_AUDIO_FORMAT="pcm" # Override for TTS only (default: pcm)
export VOICEMODE_STT_AUDIO_FORMAT="mp3" # Override for STT upload
# Format-specific quality settings
export VOICEMODE_OPUS_BITRATE="32000" # Opus bitrate (default: 32kbps)
export VOICEMODE_MP3_BITRATE="64k" # MP3 bitrate (default: 64k)
Audio Format Configuration
Voice Mode uses PCM audio format by default for TTS streaming for optimal real-time performance:
- PCM (default for TTS): Zero latency, best streaming performance, uncompressed
- MP3: Wide compatibility, good compression for uploads
- WAV: Uncompressed, good for local processing
- FLAC: Lossless compression, good for archival
- AAC: Good compression, Apple ecosystem
- Opus: Small files but NOT recommended for streaming (quality issues)
The audio format is automatically validated against provider capabilities and will fallback to a supported format if needed.
Local STT/TTS Services
For privacy-focused or offline usage, Voice Mode supports local speech services:
- Whisper.cpp - Local speech-to-text with OpenAI-compatible API
- Kokoro - Local text-to-speech with multiple voice options
These services provide the same API interface as OpenAI, allowing seamless switching between cloud and local processing.
OpenAI API Compatibility Benefits
By strictly adhering to OpenAI's API standard, Voice Mode enables powerful deployment flexibility:
- 🔀 Transparent Routing: Users can implement their own API proxies or gateways outside of Voice Mode to route requests to different providers based on custom logic (cost, latency, availability, etc.)
- 🎯 Model Selection: Deploy routing layers that select optimal models per request without modifying Voice Mode configuration
- 💰 Cost Optimization: Build intelligent routers that balance between expensive cloud APIs and free local models
- 🔧 No Lock-in: Switch providers by simply changing the
BASE_URL- no code changes required
Example: Simply set OPENAI_BASE_URL to point to your custom router:
export OPENAI_BASE_URL="https://router.example.com/v1"
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-key"
# Voice Mode now uses your router for all OpenAI API calls
The OpenAI SDK handles this automatically - no Voice Mode configuration needed!
Architecture
┌─────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ Claude/LLM │ │ LiveKit Server │ │ Voice Frontend │
│ (MCP Client) │◄────►│ (Optional) │◄───►│ (Optional) │
└─────────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ └─────────────────────┘
│ │
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ Voice MCP Server │ │ Audio Services │
│ • converse │ │ • OpenAI APIs │
│ • listen_for_speech│◄───►│ • Local Whisper │
│ • check_room_status│ │ • Local TTS │
│ • check_audio_devices └──────────────────┘
└─────────────────────┘
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- No microphone access: Check system permissions for terminal/application
- WSL2 Users: See WSL2 Microphone Access Guide
- UV not found: Install with
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh - OpenAI API error: Verify your
OPENAI_API_KEYis set correctly - No audio output: Check system audio settings and available devices
Debug Mode
Enable detailed logging and audio file saving:
export VOICEMODE_DEBUG=true
Debug audio files are saved to: ~/voicemode_recordings/
Audio Diagnostics
Run the diagnostic script to check your audio setup:
python scripts/diagnose-wsl-audio.py
This will check for required packages, audio services, and provide specific recommendations.
Audio Saving
To save all audio files (both TTS output and STT input):
export VOICEMODE_SAVE_AUDIO=true
Audio files are saved to: ~/voicemode_audio/ with timestamps in the filename.
Documentation
📚 Read the full documentation at voice-mode.readthedocs.io
Getting Started
- Integration Guides - Step-by-step setup for all supported tools
- Configuration Guide - Complete environment variable reference
Development
- Using uv/uvx - Package management with uv and uvx
- Local Development - Development setup guide
- Audio Formats - Audio format configuration and migration
- Statistics Dashboard - Performance monitoring and metrics
Service Guides
- Whisper.cpp Setup - Local speech-to-text configuration
- Kokoro Setup - Local text-to-speech configuration
- LiveKit Integration - Real-time voice communication
Troubleshooting
- WSL2 Microphone Access - WSL2 audio setup
- Migration Guide - Upgrading from older versions
Links
- Website: getvoicemode.com
- Documentation: voice-mode.readthedocs.io
- GitHub: github.com/mbailey/voicemode
- PyPI: pypi.org/project/voice-mode
- npm: npmjs.com/package/voicemode
Community
- Discord: Join our community
- Twitter/X: @getvoicemode
- YouTube: @getvoicemode
See Also
- 🚀 Integration Guides - Setup instructions for all supported tools
- 🔧 Configuration Reference - Environment variables and options
- 🎤 Local Services Setup - Run TTS/STT locally for privacy
- 🐛 Troubleshooting - Common issues and solutions
License
MIT - A Failmode Project
Voice MCP Reviews
Login Required
Please log in to share your review and rating for this MCP.
Related MCP Servers
Discover more MCP servers with similar functionality and use cases
Zed
OfficialClientby zed-industries
Provides real-time collaborative editing powered by Rust, enabling developers to edit code instantly across machines with a responsive, GPU-accelerated UI.
Cline
Clientby cline
Provides autonomous coding assistance directly in the IDE, enabling file creation, editing, terminal command execution, browser interactions, and tool extension with user approval at each step.
Continue
Clientby continuedev
Provides continuous AI assistance across IDEs, terminals, and CI pipelines, offering agents, chat, inline editing, and autocomplete to accelerate software development.
GitHub MCP Server
by github
Enables AI agents, assistants, and chatbots to interact with GitHub via natural‑language commands, providing read‑write access to repositories, issues, pull requests, workflows, security data and team activity.
Goose
Clientby block
Automates engineering tasks by installing, executing, editing, and testing code using any large language model, providing end‑to‑end project building, debugging, workflow orchestration, and external API interaction.
Roo Code
OfficialClientby RooCodeInc
An autonomous coding agent that lives inside VS Code, capable of generating, refactoring, debugging code, managing files, running terminal commands, controlling a browser, and adapting its behavior through custom modes and instructions.
Mcp Agent
Clientby lastmile-ai
A lightweight, composable framework for building AI agents using Model Context Protocol and simple workflow patterns.
Firebase CLI
by firebase
Provides a command‑line interface to manage, test, and deploy Firebase projects, covering hosting, databases, authentication, cloud functions, extensions, and CI/CD workflows.
Gptme
Clientby gptme
Empowers large language models to act as personal AI assistants directly inside the terminal, providing capabilities such as code execution, file manipulation, web browsing, vision, and interactive tool usage.